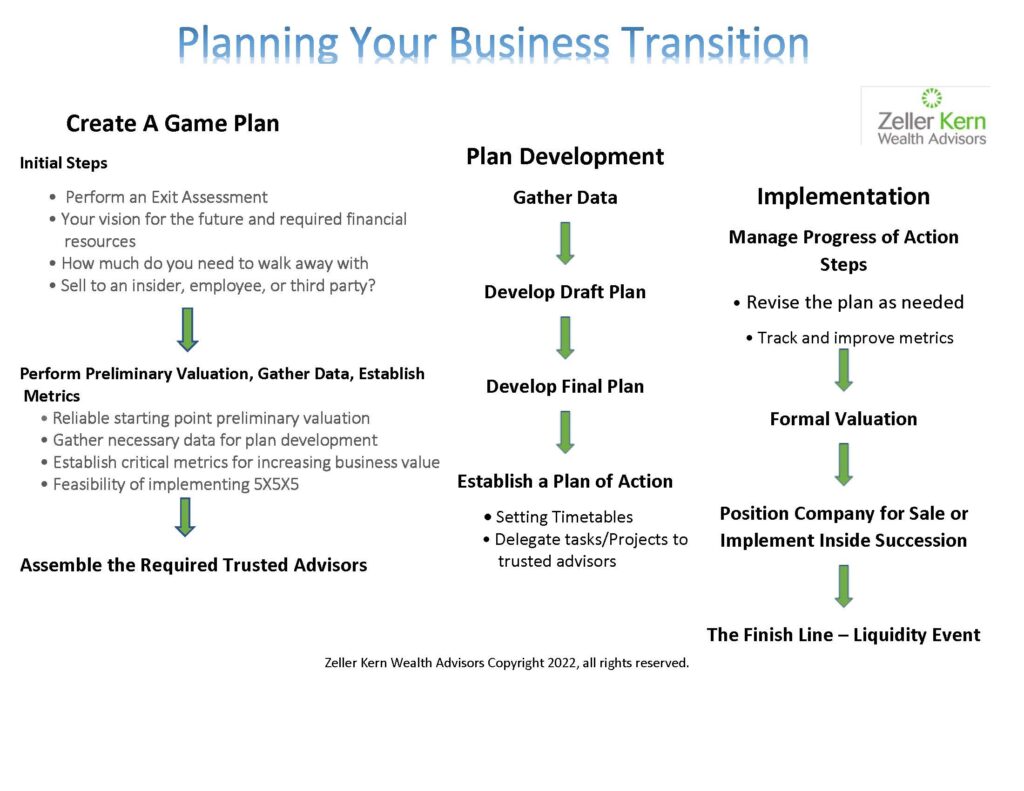
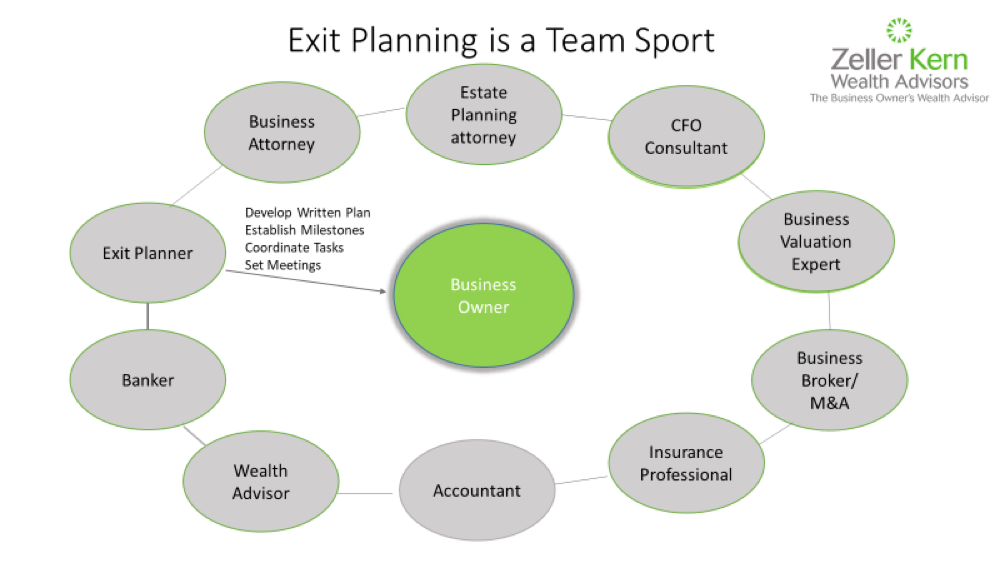
One of the most common sales pitches you might hear from someone claiming to help you “enhance value” goes something like this:
“I’ve reviewed your company and believe it’s worth $4.2 million today. With the right planning, it could be worth $7.7 million. Would you rather exit with $4.2 million or $7.7 million?”
That’s not really a question—it’s a setup. Of course, no business owner would willingly choose the smaller number. But the real issue isn’t which number you prefer. It’s what it actually takes to bridge that gap—and whether you’re being given a full picture.
Are You Falling for the Planning Fallacy?

There’s a psychological term for this overly optimistic way of thinking: the planning fallacy.
A private equity investors group I follow, Chenmark.com, once cited a study published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology that perfectly illustrates the concept:
From a psychological perspective, the planning fallacy can perhaps be studied most profitably at the level of daily activities. Consider one familiar example: Academics who carry home a stuffed briefcase full of work on Fridays, fully intending to complete every task, are often aware that they have never gone beyond the first one or two jobs on any previous weekend.
The intriguing aspect of this phenomenon is the ability of people to hold two seemingly contradictory beliefs: Although aware that most of their previous predictions were overly optimistic, they believe that their current forecasts are realistic. It seems that people can know the past and still be doomed to repeat it.
What’s fascinating is that they know this pattern. Yet, every weekend, they’re sure this time will be different. Business owners do something similar: despite knowing how long things usually take (and how unpredictable growth can be), we still believe “this time” will follow our best-case forecast.
You may hear that big valuation potential and think, “Yes, that’s what I’ve always wanted—to grow the company by 83%! I just needed a plan.”
But a plan alone isn’t enough. It’s a start—but not the whole story.
What Really Closes the Gap?
Let’s reframe that optimistic pitch with a more realistic one:
“To grow from $4.2 million to $7.7 million in five years, you’ll need proper planning, dedicated effort, some strategic hires, and reinvesting a significant portion of your profits. That requires growing the business 19% annually—starting immediately. That’s more than double your best year to date. If you spend a year building that foundation first, then you’d need to grow at least 25% annually over the next four years. If you keep growing at your best year’s rate of 7.5%, it will take over 12 years to reach that goal.”
Those are the facts. And the reality is that very few business owners hit those growth rates without serious changes—and trusted advisors to help them.
The Power of Perspective (and the Right Guide)
You may have a solid company. It supports your lifestyle, your employees, and your reputation. Maybe you’ve even dreamed of taking it further. But the risks, the effort, or the lack of a clear roadmap have held you back.
That’s exactly where experienced advisors come in—not to promise easy gains, but to help you map a realistic path to your goals. They help align what you want (your proceeds), with what you’re willing to do (your effort), in the time you have left (your exit timeline).
In our work, we use a Value Gap coaching model that considers four essential pieces:
1. Current business value
2. Your desired outcome—not just “more,” but a specific number
3. The timeframe in which you want to exit
4. The required growth rate to get there
Often, once those last two are on the table, the conversation changes. It’s not just about the money—it’s about what you’re willing and able to do to get there.
The real planning fallacy? Believing it’s just about hitting a number. The truth is, getting the outcome you want depends on understanding the full picture—and working with an advisor who helps you navigate it honestly, strategically, and with clarity.
John F. Dini develops transition and succession strategies that allow business owners to exit their companies on their own schedule, with the proceeds they seek and complete control over the process. He takes a coaching approach to client engagements, focusing on helping owners of companies with $1M to $250M in revenue achieve both their desired lifestyles and legacies.